As the electric vehicle (EV) market continues to evolve, a new dynamic is unfolding in China, the world’s largest EV market. While Tesla has long enjoyed a favorable position, its Shanghai gigafactory now faces a growing threat. With the rapid rise of BYD, a homegrown Chinese electric vehicle manufacturer, there is increasing speculation that the Chinese government may shut down Tesla’s operations in Shanghai, allowing its own EV giant to take the lead.
This move would not only shift the balance of power in China’s auto industry but could have sweeping implications for Tesla’s global operations.
Tesla’s gigafactory in Shanghai, established in January 2019, has played a pivotal role in the company’s success. The factory is responsible for producing over half of Tesla's annual global output of roughly 1.8 million vehicles, including the Model 3 and Model Y.
As Tesla’s primary manufacturing hub outside the United States, the Shanghai factory has been instrumental in the company’s ability to dominate the global EV market. It has bolstered Tesla’s market share, particularly in China, and helped propel Elon Musk to his position as the richest person in the world.
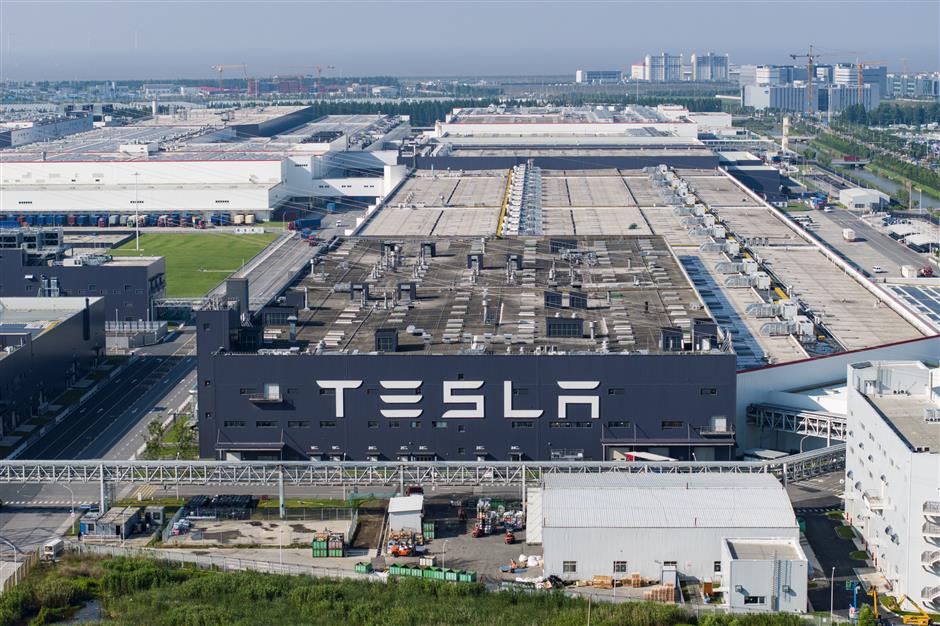

However, Tesla’s reliance on its Shanghai factory for both local production and export has placed the company in a precarious position. As BYD continues to assert its dominance in China’s rapidly growing EV market, the government’s favor towards BYD could lead to an increasingly hostile environment for Tesla in the region.
BYD, which stands for "Build Your Dreams," has rapidly emerged as China’s largest EV manufacturer, surpassing Tesla in several key performance metrics. The company has experienced explosive growth, with its annual vehicle sales reaching over 1 million units in the first quarter of 2025, a 60% increase from the same period in 2024.
By comparison, Tesla sold just 336,681 vehicles in the same period. In addition, BYD's net income for 2025 reached $1.26 billion, significantly outperforming Tesla’s $934 million—a 40% decline from the previous year.
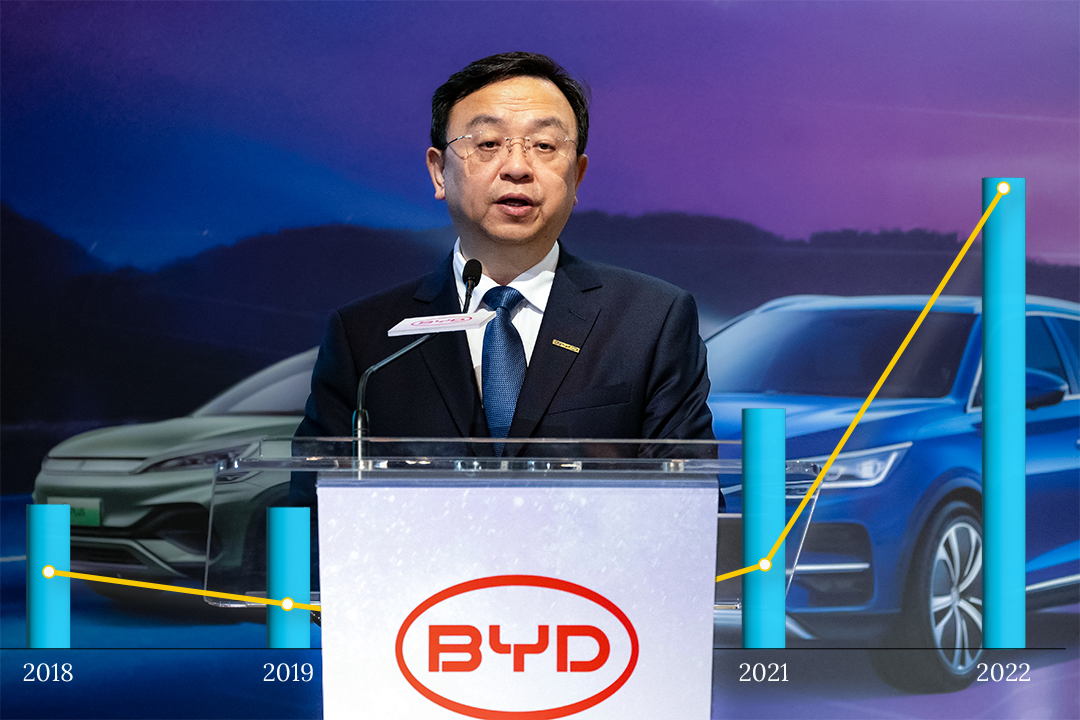

The Chinese government, recognizing BYD’s potential to become a global EV powerhouse, has provided strong support for the company, including subsidies, favorable policies, and access to local resources. This backing has allowed BYD to produce vehicles at a lower cost than Tesla, making its products more appealing to Chinese consumers.
Additionally, BYD’s wide range of electric vehicles—from compact cars to buses—has enabled the company to capture a larger share of the domestic market.
With Tesla's Shanghai factory now under increasing pressure from BYD's growing dominance, there is a real risk that the Chinese government could choose to prioritize its own homegrown EV giant over the American tech company. In fact, many industry analysts speculate that the government may push Tesla out of the region altogether to make room for BYD, a move that would align with China's broader goal of supporting domestic companies in key industries.
In the face of growing competition, BYD’s rise has been fueled by favorable government policies aimed at bolstering China’s EV industry. In addition to direct subsidies and grants, the Chinese government has offered BYD significant advantages, including reduced taxes and incentives for consumers to buy electric vehicles.
Meanwhile, Tesla’s position in China has become increasingly tenuous, partly due to its ties to the United States and its outspoken CEO, Elon Musk, whose relationship with former U.S. President Donald Trump has raised concerns among Chinese officials.
BYD’s success can also be attributed to its ability to produce vehicles at scale and offer more affordable options for Chinese consumers. The company’s EVs, such as the BYD Seal and BYD Qin, have gained significant traction due to their competitive pricing and impressive performance.
As a result, BYD has managed to surpass Tesla in sales within China, securing the top spot in the Chinese EV market. Furthermore, the company’s aggressive global expansion strategy has allowed it to gain a foothold in international markets such as Europe and Latin America.
If the Chinese government were to close Tesla’s Shanghai factory, it would have significant repercussions for the company. Tesla’s dependence on the Shanghai facility for both local sales and global exports makes it critical to the company’s ability to meet demand in key markets like Europe and the U.S.
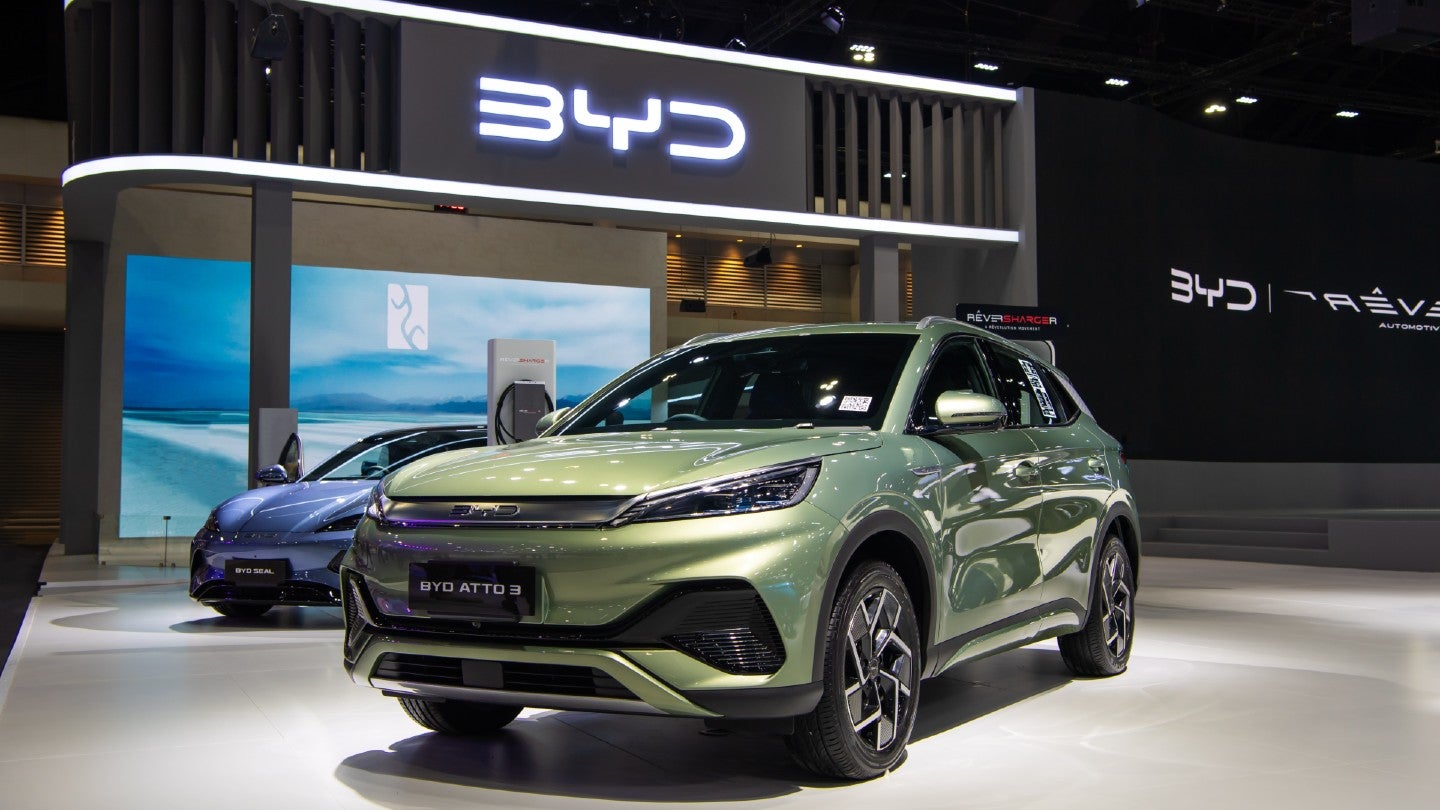

Losing this factory would lead to a drastic reduction in production capacity, forcing Tesla to find alternative production solutions, likely at a much higher cost.
A closure of the Shanghai factory would also disrupt Tesla’s entire supply chain. The factory produces not only vehicles but also key components, including batteries and electric drivetrains, for export markets.
Without access to the Shanghai facility, Tesla would face significant logistical challenges in maintaining its global operations, potentially driving up costs and delaying production timelines.
Beyond the financial implications, Tesla’s reputation in China would also suffer. As the world’s largest EV market, China plays a crucial role in shaping global demand for electric vehicles.
Losing a strong foothold in China could hinder Tesla’s growth prospects in other regions, further eroding its market share to BYD and other competitors.
BYD’s ability to capture both the domestic Chinese market and international markets positions it as a growing threat to Tesla’s market leadership. In 2025, BYD plans to double its overseas sales to over 800,000 units, expanding its reach into Europe, Latin America, and Southeast Asia.
The company’s $4.5 billion manufacturing plant in Hungary, set to produce 200,000 vehicles annually, is a key part of its strategy to penetrate the European market and compete with Tesla’s established presence in the region.
BYD’s success abroad is further boosted by its affordability and government backing. While Tesla remains the dominant player in premium EVs, BYD has been able to cater to a broader range of consumers with its diverse product offerings and lower price points.
This strategic approach has enabled BYD to thrive in a global market that is becoming increasingly price-sensitive, especially as EV adoption expands beyond wealthy consumers.

In addition to its competitive pricing, BYD has made significant strides in technological innovation. The company’s vehicles are equipped with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), including its "God's Eye" system, which is now standard on 21 of its 30 models.
This system includes features such as automated valet parking, highway driving assistance, and other autonomous driving capabilities that are comparable to Tesla’s Autopilot system. BYD’s continued focus on improving EV technology and integrating autonomous driving features further positions it as a serious competitor to Tesla.
Moreover, BYD’s focus on battery technology is a major strength. The company has shifted to using Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries, which are more affordable and safer than traditional lithium-ion batteries. This change has enabled BYD to reduce production costs and pass those savings on to consumers, making its vehicles more accessible to a broader market.

The potential closure of Tesla’s Shanghai gigafactory to make way for BYD would mark a significant turning point in the global EV market. While Tesla remains a leader in electric vehicles, the rise of BYD, with its favorable government support, innovative technologies, and cost-effective production methods, poses a growing threat to Tesla’s market position.
The Chinese government’s favor towards BYD is evident, and if Tesla’s reliance on its Shanghai factory becomes too great, it could ultimately be forced to yield to its Chinese competitor.
As the EV market continues to grow and evolve, the competition between Tesla and BYD will shape the future of the industry. For Tesla, the risk of losing its foothold in China and globally highlights the precariousness of relying too heavily on one region for production.
For BYD, the opportunity to lead the global EV market is within reach, and the company’s growing influence is set to redefine the competitive landscape of the automotive industry.



-1746587875-q80.webp)