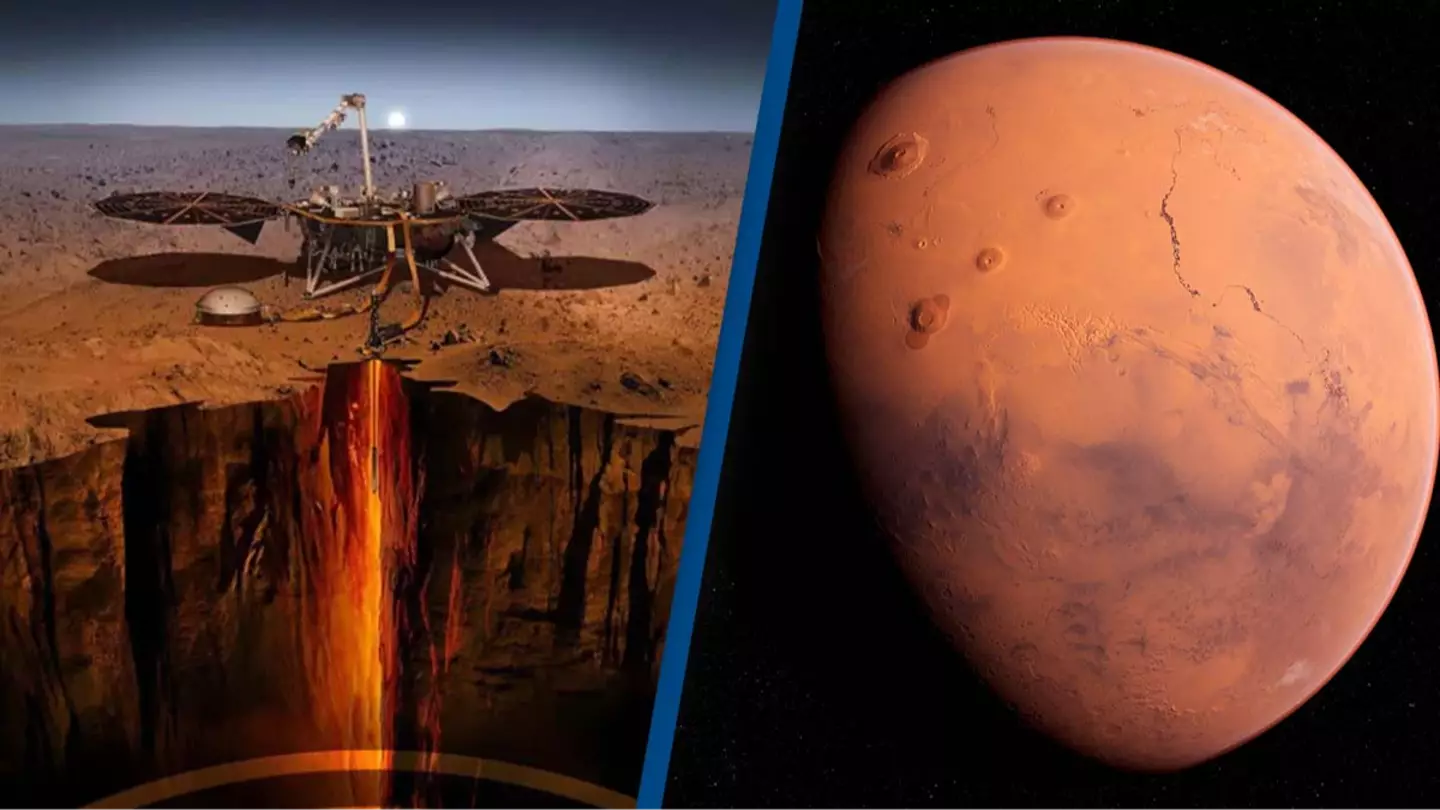
In an extraordinary breakthrough that could change the trajectory of human exploration and colonization of Mars, SpaceX has made a historic discovery on the Red Planet.
Using their cutting-edge technologies and a series of advanced missions, SpaceX’s rovers and scientific instruments have confirmed the presence of significant water reserves beneath Mars’ surface, along with a network of unexplored caves that could hold the key to future human habitation.
This discovery marks one of the most significant developments in the quest to make Mars a viable second home for humanity.
While the notion of water on Mars has been a topic of scientific speculation for decades, SpaceX’s recent findings provide concrete evidence that Mars may be far more hospitable than previously believed.
For scientists, explorers, and SpaceX alike, this breakthrough represents a monumental achievement in space exploration, with profound implications for the future of space travel and the potential for life beyond Earth.
SpaceX, the leading private aerospace company founded by Elon Musk, has long set its sights on Mars as the ultimate destination for human colonization.
Musk’s vision for a self-sustaining Martian colony has been central to the company’s mission. For years, SpaceX has worked tirelessly to develop the technologies necessary to land humans on Mars, with the Starship program at the forefront of these efforts.
Since the successful landing of the first rovers on Mars, SpaceX has made great strides in harnessing the power of autonomous exploration to better understand the Martian environment.
The company’s recent missions, which include the deployment of advanced rovers and scientific instruments, have enabled SpaceX to conduct detailed geological surveys of Mars' surface and subsurface.
The primary focus of these missions has been to search for signs of life, understand the planet’s past climate, and assess its potential for human habitation.
Among the most critical questions scientists have aimed to answer is whether Mars has access to water, which is essential for sustaining life and supporting human colonies.
The latest findings from SpaceX’s Mars missions have confirmed the existence of substantial water reserves buried beneath the surface. For years, scientists have theorized that Mars, in its distant past, may have had flowing water on its surface, with rivers, lakes, and perhaps even oceans.
However, the presence of liquid water beneath the surface has remained largely unproven until now.
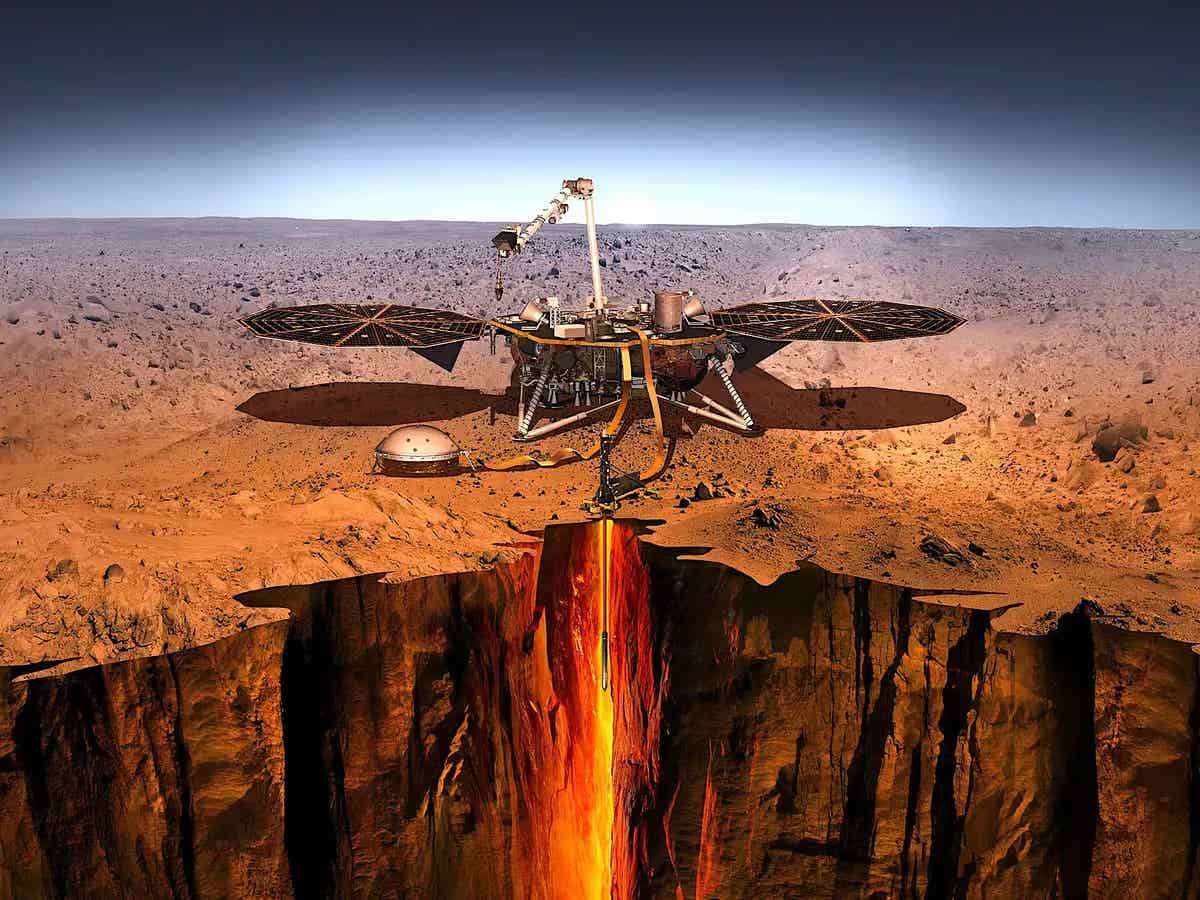
SpaceX’s most recent rover, which has been equipped with state-of-the-art geological tools and sensors, made the groundbreaking discovery. Using a combination of ground-penetrating radar and seismic imaging technology, the rover detected large reservoirs of water frozen beneath the surface.
These frozen reserves are located in several regions of Mars, with evidence suggesting they could be much more extensive than previously thought.
The water is believed to exist in the form of ice, deeply embedded within the planet’s crust. However, SpaceX’s instruments also found indications that certain regions may harbor liquid water trapped within underground aquifers.

This presents an exciting possibility: if liquid water can be accessed, it could provide a reliable resource for future human settlers, eliminating one of the most significant barriers to sustainable life on Mars.
The presence of water on Mars is a game-changer for the prospect of colonization. Not only is water essential for human survival—serving as a source of drinking water, a base for agricultural growth, and even a potential resource for fuel (through the process of electrolysis)—but it also has broader implications for the potential of life beyond Earth.
If Mars has subsurface water, it could provide a crucial environment for microbial life to exist, offering valuable clues about the potential for life on other planets.
In addition to the discovery of water, SpaceX’s rover missions have uncovered another exciting find—an extensive network of caves located deep within Mars’ surface. These caves, which were previously unknown to scientists, could play a crucial role in the future of Martian colonization.
The caves were detected using advanced imaging and radar technology, which penetrated the Martian surface to identify voids and caverns hidden below.
These caves are located in various regions of Mars, with some appearing to be quite large and interconnected, potentially forming a vast subterranean network. These caves could serve as a natural shelter for future settlers, offering protection from the harsh Martian environment above.
Mars’ surface is notoriously hostile, with extreme temperatures, intense radiation from the sun, and frequent dust storms that can last for weeks. For human settlers, these caves could offer an ideal refuge, shielding them from radiation and extreme temperatures.
The caves would also provide a stable environment for growing food, conducting scientific research, and establishing a permanent base for exploration.
The caves’ natural formation could provide a ready-made infrastructure for human colonies, eliminating the need for costly construction of above-ground habitats.
SpaceX’s team of scientists and engineers is already planning a series of robotic missions to further explore these caves and assess their suitability for human habitation.
These missions will focus on identifying potential risks, such as unstable ground or toxic gases, while also gathering data on the caves’ internal conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and air composition.
One of the most significant implications of SpaceX’s discoveries is the potential for terraforming Mars—transforming the planet’s environment to make it more Earth-like and suitable for human life.
Water and caves are critical components of any terraforming effort, as they provide the foundation for the creation of a sustainable atmosphere and climate on Mars.
While terraforming is still a distant goal, the discovery of water reserves and underground caves has brought it one step closer to reality. With access to water, SpaceX could begin the process of building closed-loop ecosystems that could support life.
The caves, in turn, could serve as the foundation for creating a stable, livable environment by controlling factors such as temperature, humidity, and radiation exposure.
In the long term, these developments could pave the way for the creation of self-sustaining colonies on Mars, capable of producing their own food, water, and energy without relying on Earth. This would mark a monumental achievement in the human quest to become a multiplanetary species.
The discovery of water and caves on Mars has far-reaching implications not only for the future of space exploration but also for the future of humanity.
SpaceX’s groundbreaking findings have opened up new possibilities for interplanetary colonization, making Mars a much more feasible destination for human settlers.
Elon Musk, the CEO of SpaceX, has long been an advocate for the colonization of Mars, viewing it as essential for ensuring humanity’s long-term survival.
With the discovery of water and the potential for underground habitation, Musk’s vision of a self-sustaining colony on Mars is now more achievable than ever before.
SpaceX is already working on developing the necessary technologies to transport humans to Mars, with the goal of launching crewed missions within the next decade.
In the coming years, SpaceX plans to send a series of missions to Mars to further explore the water reserves and caves discovered by the rovers.
These missions will focus on the construction of the first human habitats, the development of agricultural systems, and the establishment of infrastructure for resource extraction, including mining for water and minerals.
The success of these missions could mark the beginning of a new era in human space exploration, one in which humanity no longer relies solely on Earth but instead begins to thrive on other planets.
With SpaceX leading the charge, the dream of a multiplanetary civilization is now one step closer to becoming a reality.
SpaceX’s groundbreaking discovery of water and subsurface caves on Mars represents a monumental step forward in humanity’s quest to explore and colonize the Red Planet.
These findings not only confirm the presence of essential resources for human survival but also open up new possibilities for building sustainable colonies on Mars.
With the support of its advanced technologies and scientific expertise, SpaceX is poised to lead the way in the next great chapter of space exploration, bringing humanity closer to becoming a multiplanetary species.
As SpaceX continues to push the boundaries of what is possible, the future of Mars colonization has never looked more promising.